To meet market-driven quality requirements for (coated) textiles, manufacturers perform basis-weight measurement. The M-Ray technology of Hammer-IMS is available as part of Marveloc single-sensor products or integrated into Marveloc-CURTAIN turnkey systems.
The Marveloc-CURTAIN solution measures material up to 30 centimeters thick, and uses one or more fixed or traveling sensors for maximum coverage in cross-machine direction. The basis-weight measuring solution verifies material grammage (up to 1 gsm) uniformity to detect local anomalous regions with out-of-spec densities. The solutions of Hammer-IMS are fit to measure a wide range of (coated) fabrics used for applications in transportation, protective clothing, industrial roofing, awnings and canopies, furniture and seating, etc.
A calander line
A knife coating line
Textile manufacturing is a major industry. As textiles are often coated it makes sense to consult the global coated fabrics market. According to Markets and Markets, the global coated fabrics market is looking forward to an annual growth rate of more than 4%.
Textile manufacturing converts fibre into yarn, and yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into clothes. Different types of fibre are used to produce yarn. Cotton remains the most important natural fibre, followed by flax, jute, hemp as well as bast and leaf fibres. Also protein fibres (wool, silk) and synthetic fibres are widely applied. There are many variable processes available at the spinning and fabric-forming stages coupled with the complexities of the finishing and colouration processes to the production of a wide ranges of products.
The weaving process uses a loom. The lengthway threads are known as the warp, and the crossway threads are known as the weft. The warp is presented to the loom on a warp beam. The weft passes across the loom in a shuttle, that carries the yarn on a pirn.
Knitting by machine is done in two different ways: warp and weft. Weft knitting is similar in method to hand knitting with stitches all connected to each other horizontally. In a warp knit there are many pieces of yarn and there are vertical chains, zigzagged together by crossing the cotton yarn.
Textiles are often coated to obtain composites, consisting of a flexible substrate and a polymeric coating. The coating may be on one side, or on both sides with the same or a different polymeric coating per side.
Hammer-IMS helps you measure quality and process control for latex coating in carpet production. Our innovative technology, based on proprietary M-Ray electromagnetic waves, ensures accurate and safe measurements of latex grammage before and after application. This real-time monitoring allows for adaptive adjustments, maintaining consistent and high-quality latex thickness and uniformity across different carpet dimensions.
Our solutions not only enhance product quality but also minimize material waste by precisely managing latex usage. M-Ray technology contributes to your sustainability goals by eliminating the use of harmful alternatives that make use of radioactive sources, and by reducing scrap material. The integrated approach of Hammer-IMS's measuring and quality control systems brings efficiency and precision to the critical stage of latex backing in carpet manufacturing.
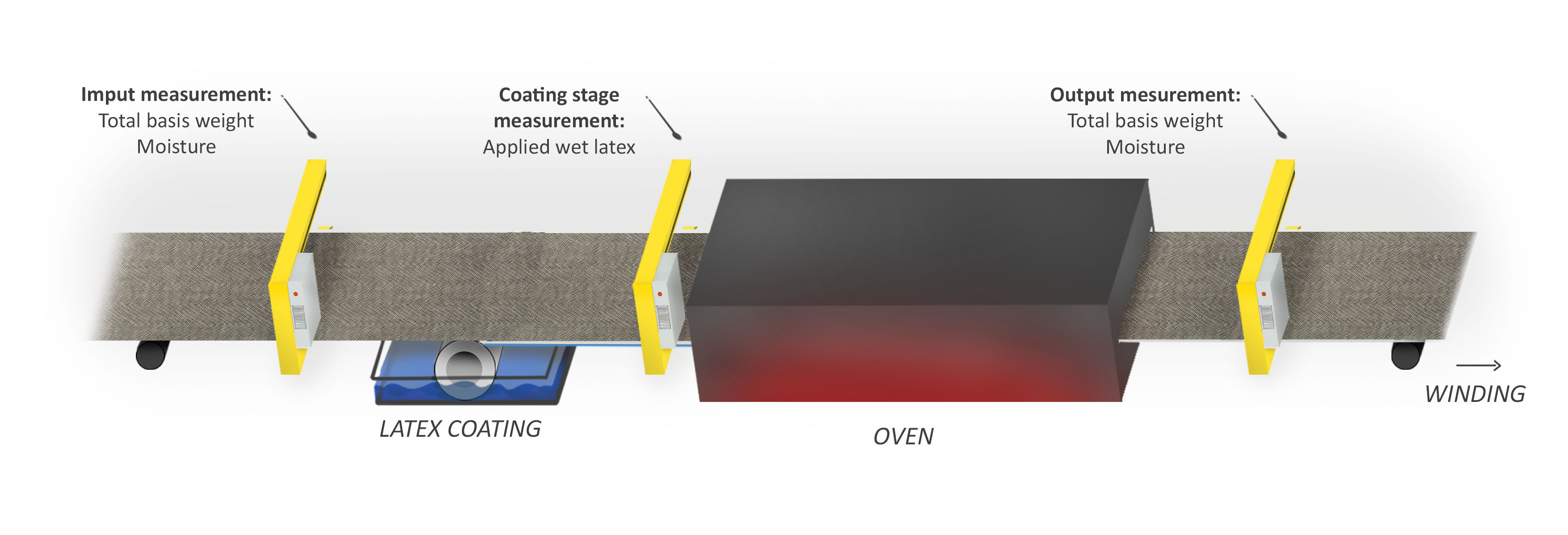
Integrated control of applied latex backing in a carpet/textile production line. The implementation of three Marveloc-CURTAIN systems allow for input measurement, coating stage measurement, and output measurement; other configurations are possible.
Surface inspection solution for detection of anomalies and defects

Machine for basis-weight measurement of flat materials
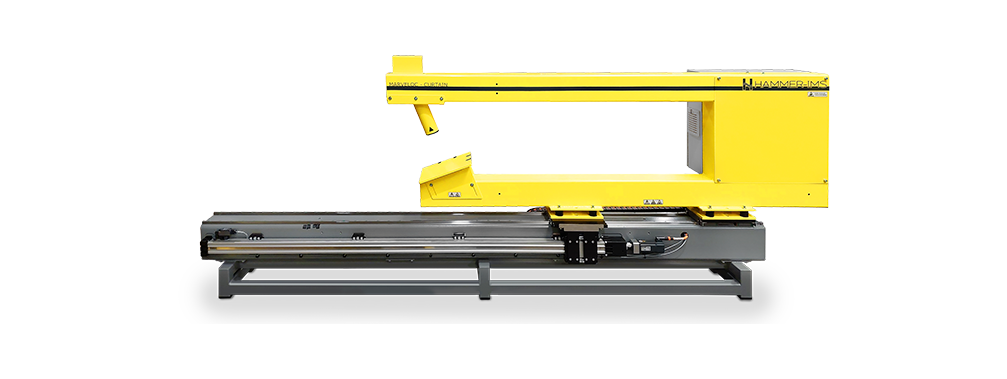
For OEM projects on basis-weight measuring by machine builders and sensor integrators

Industrial software to connect to PLC's and various information sources
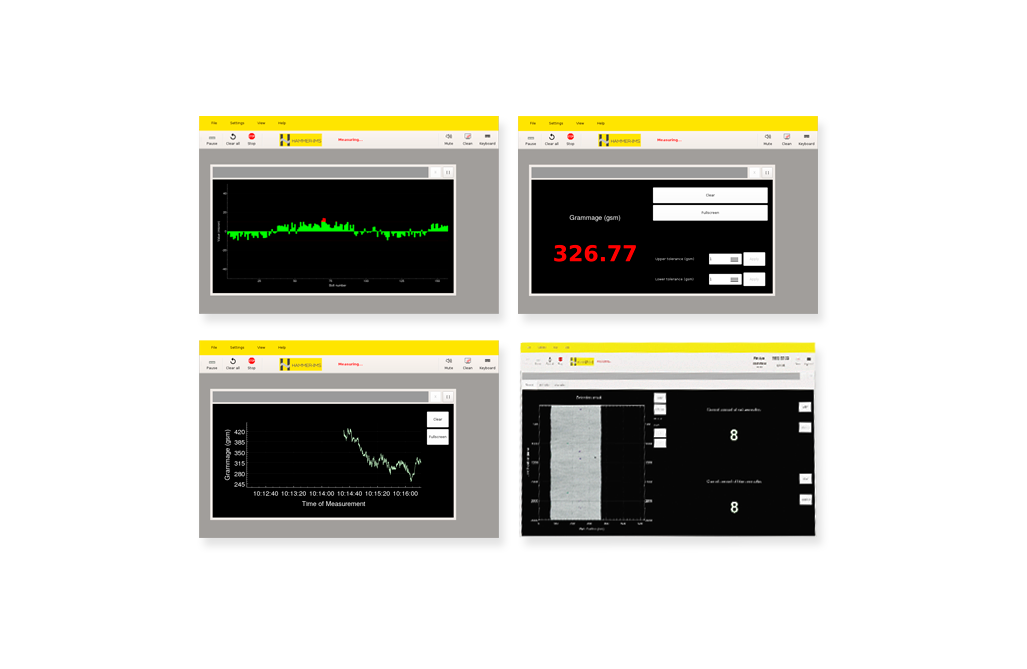
Lab devices, custom or off-the-shelf